The Latest Developments in Charging Infrastructure
As the number of electric vehicles (EVs) on the road continues to increase, so too does the demand for charging infrastructure. In recent years, there have been a number of developments in charging infrastructure that are helping to make the charging process more efficient and cost-effective.
Public Charging
One of the most significant recent developments is the increase in the number of public charging stations. Governments and private companies are investment huge amounts to make it easier for EV owners to charge their vehicles when they are away from home. This is particularly important for long-distance travel, as it allows EV owners to charge their vehicles while they are on the road.
Another development in charging infrastructure is the increasing availability of fast-charging stations. Fast-charging stations can charge an EV in a matter of minutes, as opposed to hours. This is a significant improvement over traditional charging stations, which can take several hours to charge an EV. Fast-charging stations are particularly useful for long-distance travel, as they allow EV owners to charge their vehicles quickly and continue on their journey.
The UK Government recently announced an additional £56m of funding for chargepoints. Read more here.
Access for All
Wireless charging will soon become more readily available and common feature of charging infrastructure. Wireless charging systems use electromagnetic fields to transfer energy between a charging pad and a vehicle, eliminating the need for physical connections. This technology is still in its early stages, but it has the potential to make charging even more convenient and efficient. One additional bonus of wireless charging is the additional accessibility it offers. Currently, cabled charging hugely limits those with limited mobility, removing electric vehicles as a potential vehicle type for many. Wireless charging removes the need for carrying heavy cables or reaching for charge points in awkward parking spaces or without adequate disability parking.
Read more about the work Motability have been doing to make charging more accessible here.
The Future of Charging
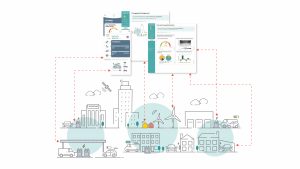
This extends further to smart charging and vehicle-to-grid (V2G), using advanced technologies such as sensors, data analytics, and communication networks to optimise the charging process. For example, smart charging stations can track the availability of power, adjust charging rates based on demand, and even communicate with EVs to coordinate charging schedules. V2G takes that one step further and turns the vehicle into a portable battery storage unit when not being driven. This means excess renewables can be used to charge the battery, with the battery discharging when demand is high. The battery is an existing asset, meaning costs are reduced as no need to purchase separate static battery storage. It also allows vehicles to trade in energy markets through implementation of a Virtual Power Plant (VPP).
If you would like to learn more about any of the technologies mentioned above, or to start your EV transition, please get in touch.

